Architecture Overview
PowerAuth architecture is designed so that the deployment can be very simple, but at the same time allows complex deployment alongside of other authentication methods (as a part of the central authentication / authorization component).
Architecture Diagram
Following diagram captures the basic deployment strategy for the PowerAuth technology.
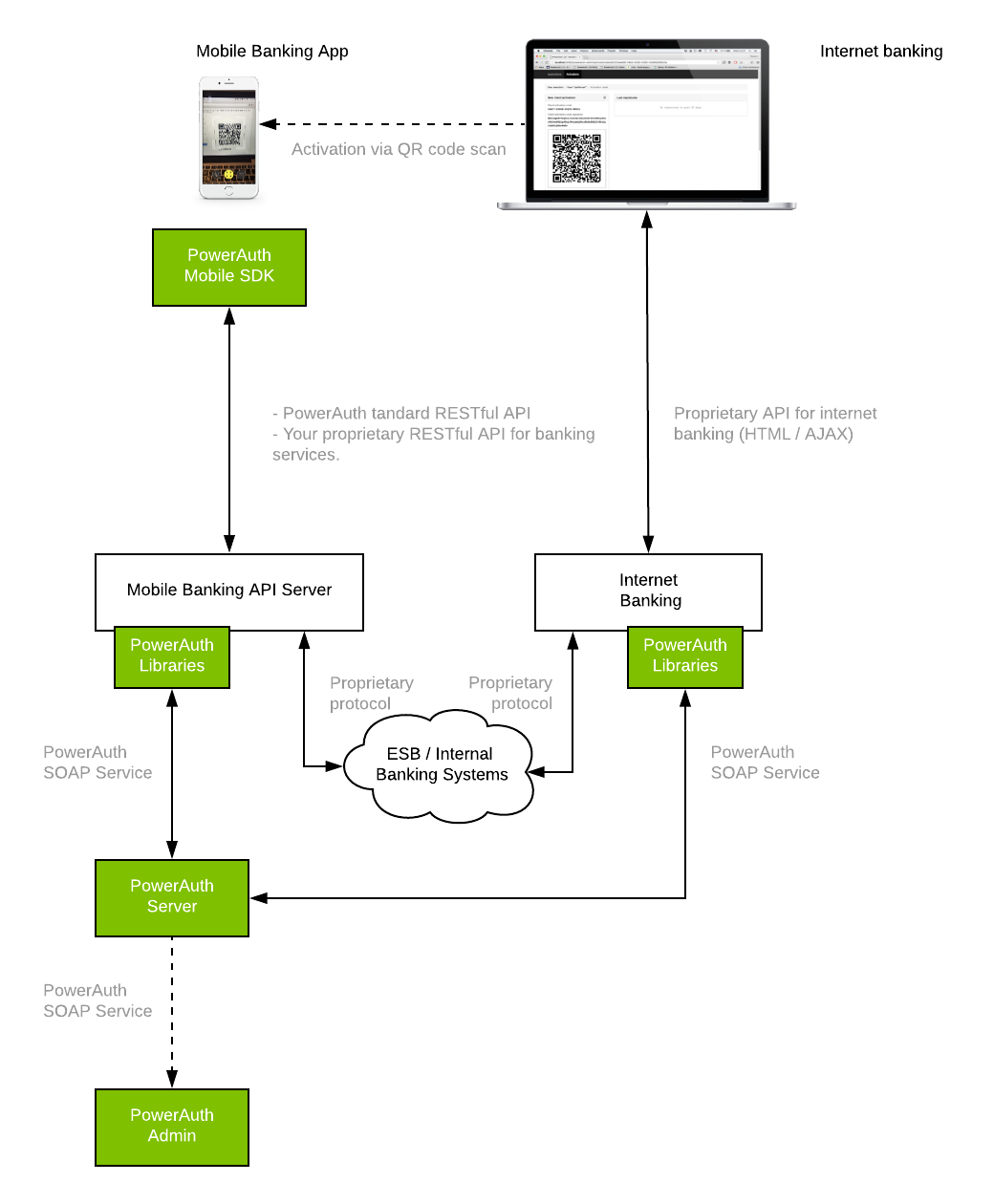
As you can see, there are only couple components present:
- Our back-end components
- Your existing back-end components
- Our integration libraries for your back-end components
- Our mobile SDK for iOS and Android apps
Our Back-End Components
PowerAuth Deployment requires installation of just one easy to deploy component.
- PowerAuth Server
- The core server component that manages activated devices, enables the activation process, verifies signatures and keeps system configuration.
- Component communicates using SOAP or REST services.
- Documentation:
- PowerAuth Admin (optional)
- Simple GUI admin for managing the PowerAuth Server.
- Documentation:
Your Back-End Components
PowerAuth installation has impact on several of your components:
- Mobile Banking API application - Application that publishes API that is consumed by the mobile clients.
- Activation Channels - Various types of applications used to activate PowerAuth Client, for example the internet banking, ATM interface, branch applications, etc.
- Internal bank systems / ESB - Of course, you can use any systems to proxy PowerAuth Server services.
Our Back-End Integration Libraries
To simplify deployment, PowerAuth brings ready-to-use libraries for Java EE / Spring, namely:
- Easy to use PowerAuth Server SOAP service client (Axis2 or Spring-WS)
- Documentation:
- High-level integration libraries that publish all required services and simplify signature validation (Java EE or Spring)
- Documentation:
Our Mobile SDK for iOS or Android
You can integrate PowerAuth easily with your mobile app using our high-level SDK.
- Documentation:
Last updated on Dec 04, 2019 (14:42)
Edit on Github
Send Feedback
