Device Activation
With ActivationService you can onboard PowerAuth with just a piece of user information like his email, phone number, or login name.
PowerAuth enrolled in such a way will need further user verification until fully operational (able to sign operations).
Example app flow
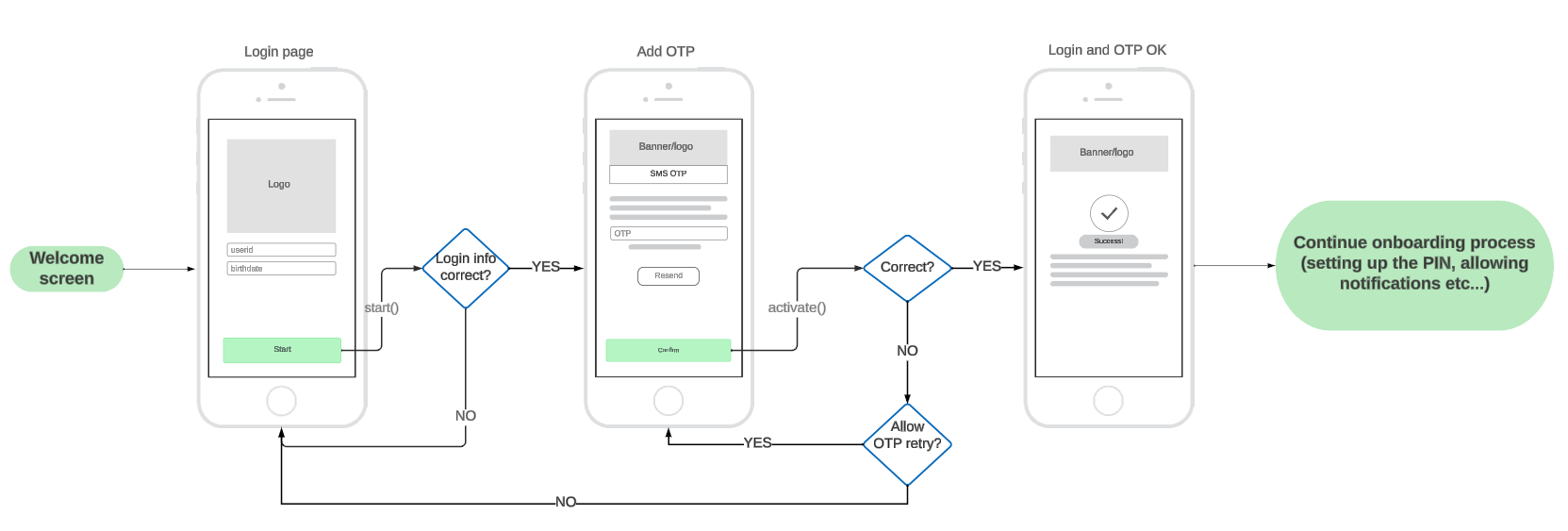
Creating an instance
To create an instance you will need a PowerAuthSDK instance that is ready to be activated, application Context, and configured OkHttpClient. Optionally, you can choose if the activation process will persist between instance re-creation (for example app restart).
Example:
val powerAuth = PowerAuthSDK
.Builder(...)
.build(appContext)
val activationService = ActivationService(
"https://sever.my/path/", // identityserver URL
appContext, // application context
OkHttpClient.Builder(), // okhttp client that performs networking
powerAuth
)
Retrieving the status
To figure out if the activation process has already started and what is the status, you can use hasActiveProcess().
/**
* If the activation process is in progress.
*
* Note that when the result is `true` it can be already discontinued on the server.
* Calling `status` in such case is recommended.
*/
fun hasActiveProcess(): Bool
If the process was started, you can verify its status by calling the status function. You can show an appropriate UI to the user based on this status.
/**
* Retrieves the status of the onboarding activation.
*
* @param callback Callback with the result.
*/
fun status(callback: (ActivationResult<Status>) -> Unit)
Status possible values.
enum class Status {
/** Activation is in the progress */
ACTIVATION_IN_PROGRESS,
/** Activation was already finished, not waiting for the verification */
VERIFICATION_IN_PROGRESS,
/** Activation failed */
FAILED,
/** Both activation and verification were finished */
FINISHED;
}
Example status check after app startup
class MyUserService {
// prepared service
private lateinit var activationService: ActivationService
fun verifyStatus() {
if (!activationService.hasActiveProcess()) {
// no active process, show
return
}
activationService.status { result ->
result.onSuccess { status ->
when (status) {
ActivationService.Status.ACTIVATION_IN_PROGRESS -> {
// activation is in progress, continue with OTP and `activate` method
}
ActivationService.Status.VERIFICATION_IN_PROGRESS -> {
// verification is in progress, continue with WDOVerificationService
}
ActivationService.Status.FINISHED -> {
// the process is finished and PowerAuthSDK instance activated
// show PIN login or other "default activated screen"
}
ActivationService.Status.FAILED -> {
// the activation failed (for example expired or was removed from the server),
// start again
}
}
}.onFailure { t ->
// handle failure (internet not working, server down, etc..)
}
}
}
}
Starting the process
To start the activation process, you can use any credentials that are sufficient for you that identify the user.
Often, such data are user email, phone number, or userID with a combination of date of birth. The definition of such data is up to your server implementation and requirements.
To start the activation, use the start function.
/**
* Starts onboarding activation with provided credentials.
*
* @param T Type that represents user credentials.
* @param credentials Object with credentials. Which credentials are needed should be provided by a system/backend provider.
* @param processType The process type identification. If not specified, the default process type will be used.
* @param callback Callback with the result.
*/
fun <T> start(credentials: T, processType: String?, callback: (ActivationResult<Unit>) -> Unit)
Example
data class UserData(
val userID: String,
val birthDate: String
)
class MyUserService {
// prepared service
private lateinit var activationService: ActivationService
private lateinit var processType: String = "ONBOARDING"
fun startActivation(id: String, bday: String) {
val data = UserData(id, bday)
activationService.start(data, processType) { result ->
result.onSuccess {
// success, continue with `activate()`
// at this moment, the `hasActiveProcess` starts return true
}.onFailure {
// show error to the user
}
}
}
}
Creating the activation
To activate the user (activating the PowerAuthSDK instance), data retrieved from the process start can be used with additional OTP. The OTP is usually sent via SMS, email, or other channel.
To decide if the OTP is needed, you can use the Configuration API or have it hardcoded.
Use the activate function to create the activation.
/**
* Activates PowerAuthSDK instance that was passed in the initializer.
*
* @param otp OTP code received by the user (via SMS or email). Optional when not required.
* @param activationName Name of the activation. Device name by default.
* @param callback Callback with the result.
*/
fun activate(
otp: String?,
activationName: String = Build.MODEL,
callback: (ActivationResult<CreateActivationResult>) -> Unit
)
Example implementation:
class MyUserService {
// prepared service
private lateinit var activationService: ActivationService
fun activate(smsOTP: String) {
activationService.activate(smsOTP) { result ->
result.onSuccess {
// PowerAuthSDK instance was activated.
// At this moment, navigate the user to
// the PIN keyboard to finish the PowerAuthSDK initialization.
// For more information, follow the PowerAuthSDK documentation.
}.onFailure {
if (it is FailedApiException && it.allowOnboardingOtpRetry() == true) {
// User entered the wrong OTP, prompt for a new one.
// Remaining OTP attempts count: it.onboardingOtpRemainingAttempts()
} else {
// show error UI
}
}
}
}
}
Canceling the process
To cancel the process, just call the cancel function.
/**
* Cancels the process.
*
* @param forceCancel When true, the process will be canceled in the SDK even when fails on the backend. `true` by default.
* @param callback Callback with the result.
*/
fun cancel(forceCancel: Boolean = true, callback: (ActivationResult<Unit>) -> Unit)
OTP resend
In some cases, you need to resent the OTP:
- OTP was not received by the user (for example when the email ends in the spam folder).
- OTP expired.
For such cases, use the resendOTP function.
/**
* Requests OTP resend.
*
* @param callback Callback with the result.
*/
fun resendOtp(callback: (ActivationResult<Unit>) -> Unit)
Errors
All functions that can return an exception are of type ActivationService.Fail that contains cause: ApiError - more about these ApiError errors can be found in the networking library documentation.
There are 3 custom exceptions that this service is adding:
Custom Exception in the cause |
Description |
|---|---|
ActivationInProgressException |
Activation is already in progress. |
ActivationNotRunningException |
Activation was not started. |
CannotActivateException |
PowerAuth instance cannot start the activation (probably already activated). |
Advanced usage
For advanced activation workflows, the ActivationService also provides a
createActivationBuilder(...) helper method that prepares a
PowerAuthActivation.Builder for the current onboarding process.
This builder can be further customized if needed and then passed directly to
PowerAuthSDK.createActivation(...).
This approach is optional and intended only for advanced use cases.
The standard activate(...) method should be sufficient for most integrations.
class MyUserService {
// prepared service
private lateinit var activationService: ActivationService
fun activateWithCustomData(otp: String?) {
val builder = activationService.createActivationBuilder(
otp = otp,
activationName = "Petr's iPhone"
) ?: return
// Optional: customize the activation builder
// e.g. add custom attributes or modify activation parameters
// builder.setCustomAttributes(...)
// builder.setExtras(...)
powerAuthSDK.createActivation(
builder.build(),
object : ICreateActivationListener {
override fun onActivationCreateSucceed(result: CreateActivationResult) {
// PowerAuthSDK instance was activated successfully
}
override fun onActivationCreateFailed(t: Throwable) {
// Handle activation failure
}
}
)
}
}
