Activation Status
PowerAuth Client may need to check for an activation status, so that it can determine if it should display UI for non-activated state (registration form), blocked state (how to unblock tutorial) or active state (login screen). To facilitate this use-case, PowerAuth Standard RESTful API publishes a /pa/v3/activation/status endpoint.
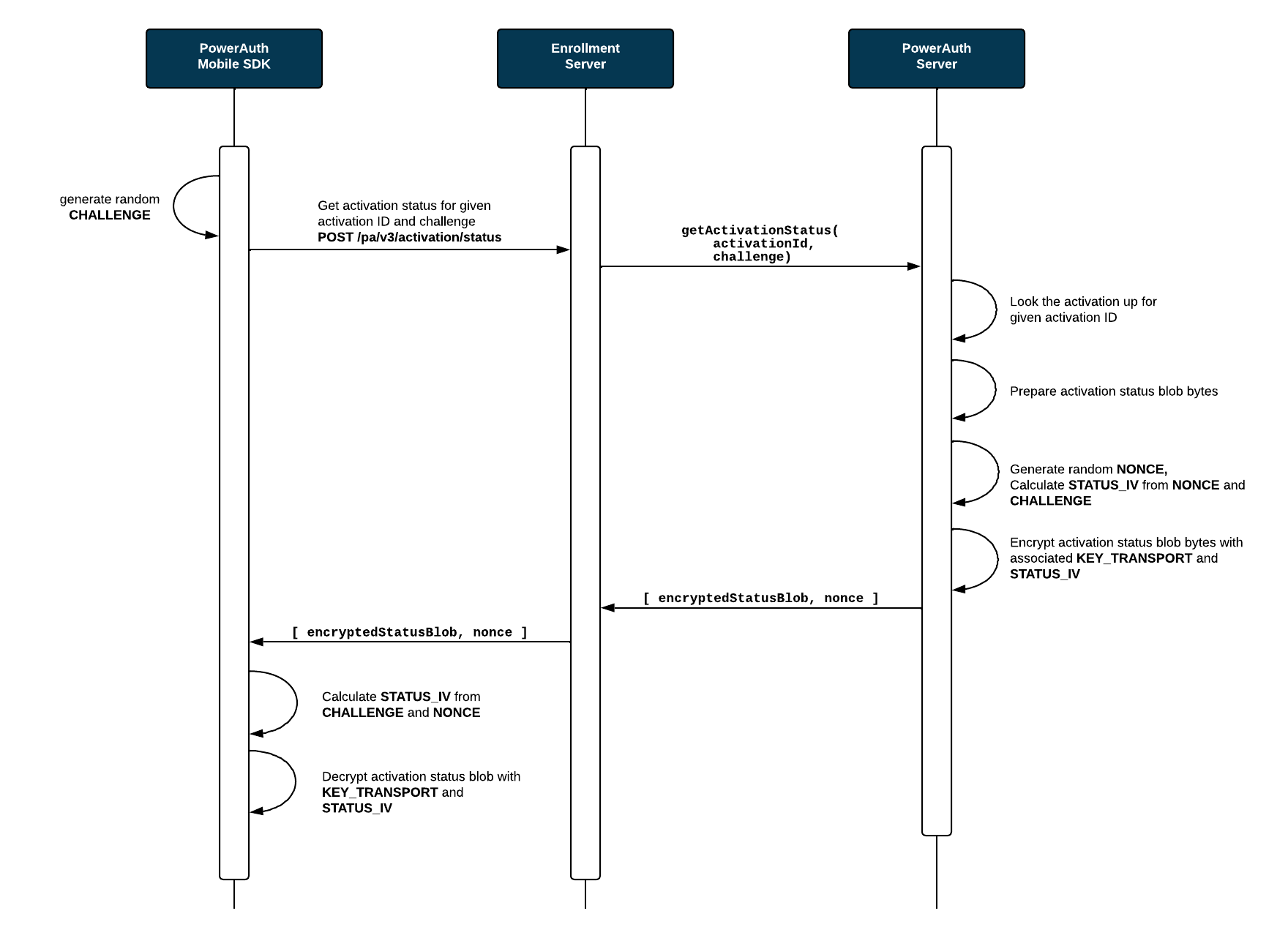
Checking for an activation status is simple. Client needs to prepare a HTTP request with an activation ID and random STATUS_CHALLENGE. Server processes the request and sends back the response with activation status blob and random STATUS_NONCE. Activation status blob is an encrypted binary blob that encodes the activation status. Key KEY_TRANSPORT and STATUS_IV is used to encrypt the activation blob.
Status Check Sequence
The following sequence diagram shows the activation status check in more detail.
Status Blob Encryption
- Both, client and server calculate
KEY_TRANSPORT_IVas:SecretKey KEY_TRANSPORT_IV = KDF.derive(KEY_TRANSPORT, 3000) - Client choose random 16 bytes long
STATUS_CHALLENGEand send that value to the server:byte[] STATUS_CHALLENGE = Generator.randomBytes(16) - Server choose random 16 bytes long
STATUS_NONCEand calculatesSTATUS_IVas:byte[] STATUS_NONCE = Generator.randomBytes(16) byte[] STATUS_IV_DATA = ByteUtils.concat(STATUS_CHALLENGE, STATUS_NONCE) byte[] STATUS_IV = KeyConversion.getBytes(KDF_INTERNAL.derive(KEY_TRANSPORT_IV, STATUS_IV_DATA)) - Server uses
KEY_TRANSPORTas key andSTATUS_IVas IV to encrypt the status blob:encryptedStatusBlob = AES.encrypt(statusBlob, STATUS_IV, KEY_TRANSPORT, "AES/CBC/NoPadding") - Server sends
encryptedStatusBlobandSTATUS_NONCEas response to the client. - Client receives
encryptedStatusBlobandSTATUS_NONCEand calculates the sameSTATUS_IVand then decrypts the status data:byte[] STATUS_IV_DATA = ByteUtils.concat(STATUS_CHALLENGE, STATUS_NONCE) byte[] STATUS_IV = KeyConversion.getBytes(KDF_INTERNAL.derive(KEY_TRANSPORT_IV, STATUS_IV_DATA)) byte[] statusBlob = AES.decrypt(encryptedStatusBlob, STATUS_IV, KEY_TRANSPORT, "AES/CBC/NoPadding")
Status Blob Format
When obtaining the activation status, application receives the binary status blob. Structure of the 32B long status blob is the following (without newlines):
0xDEC0DED1 1B:${STATUS} 1B:${CURRENT_VERSION} 1B:${UPGRADE_VERSION}
5B:${RESERVED} 1B:${CTR_BYTE} 1B:${FAIL_COUNT} 1B:${MAX_FAIL_COUNT}
1B:${CTR_LOOK_AHEAD} 16B:${CTR_DATA_HASH}
where:
- The first 4 bytes (
0xDE 0xC0 0xDE 0xD1) are basically a fixed prefix.- Note that the last byte of this constant also represents the version of the status blob format. If we decide to change the status blob significantly, then the value will be changed to
0xD2,0xD3, etc.
- Note that the last byte of this constant also represents the version of the status blob format. If we decide to change the status blob significantly, then the value will be changed to
${STATUS}- A status of the activation record, it can be one of following values:0x01 - CREATED0x02 - PENDING_COMMIT0x03 - ACTIVE0x04 - BLOCKED0x05 - REMOVED
${CURRENT_VERSION}- 1 byte representing current version of crypto protocol, it can be one of following values:0x02- PowerAuth protocol version2.x0x03- PowerAuth protocol version3.x
${UPGRADE_VERSION}- 1 byte representing maximum protocol version supported by the PowerAuth Server. The set of possible values is identical to${CURRENT_VERSION}${RESERVED}- 5 bytes reserved for the future use.${CTR_BYTE}- 1 byte representing the least significant byte from current value of counter, calculated as:byte CTR_BYTE = (byte)(CTR & 0xFF);${FAIL_COUNT}- 1 byte representing information about the number of failed attempts at the moment.${MAX_FAIL_COUNT}- 1 byte representing information about the maximum allowed number of failed attempts.${CTR_LOOK_AHEAD}- 1 byte representing constant for a look ahead window, used on the server to validate the signature.${CTR_DATA_HASH}- 16 bytes containing hash from current value of a hash-based counter:SecretKey KEY_TRANSPORT_CTR = KDF.derive(KEY_TRANSPORT, 4000); byte[] CTR_DATA_HASH = KeyConversion.getBytes(KDF_INTERNAL.derive(KEY_TRANSPORT_CTR, CTR_DATA));
