DocuCheck Usage
This document describes all command line options supported in DocuCheck tool.
Basic usage
The basic tool usage is simple. Type DocuCheck with a combination of parameters, for example:
$ DocuCheck -h
Prints embedded command’s help to the console:
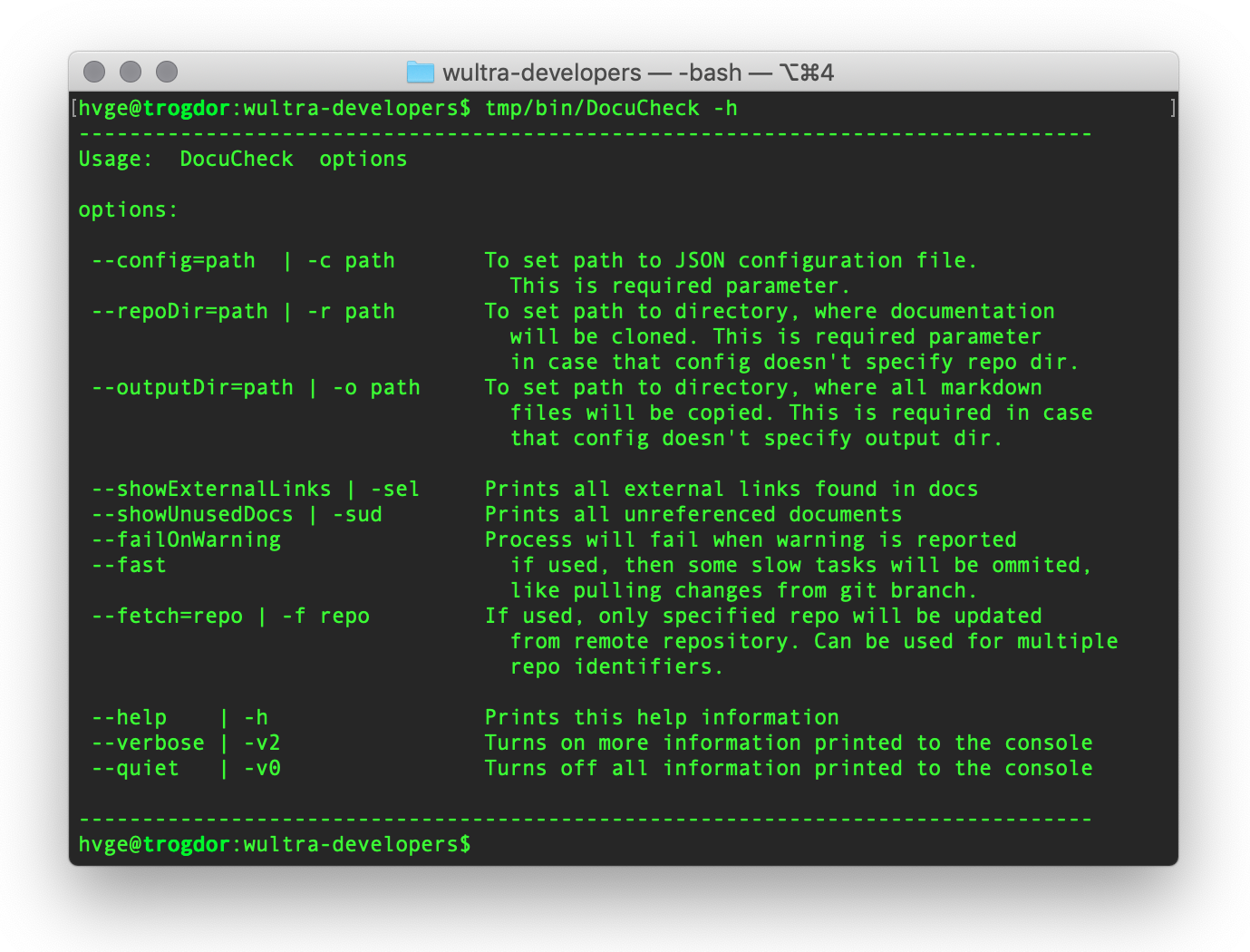
Command parameters
-hor--help- Prints help information embedded in the command
--config=pathor-c path- Defines
pathto JSON configuration file. - This parameter is required and cannot be omitted.
- Defines
--repoDir=pathor-r path- Defines
pathto a repository cache directory, where all documentation source repositories will be cloned. - If JSON configuration doesn’t specify this folder, then the parameter must be specified.
- Defines
--outputDir=pathor-o path- Defines
pathto output folder, where all final documentation will be prepared. - If JSON configuration doesn’t specify this folder, then the parameter must be specified.
- Defines
--showExternalLinksor-sel- Tells
DocuCheckto print all links to external webpages, found in the documentation. - This option is useful in case that you have renamed some of your projects (or you have changed email in documentation) and you want to find whether there’s still link to that old repository. This kind of situation cannot be detected automatically by the tool and that’s why you should print the links and do your manual check.
- Tells
--showUnusedDocsor-sud- Tells
DocuCheckto print all documents in the documentation which has no reference from another documents. This is useful when you want to find unused parts of your documentation.
- Tells
--failOnWarning- If set, and some WARNING is reported, then the return code from
DocuCheckis non-zero. This situation is then typically treated as failure in bash scripts.
- If set, and some WARNING is reported, then the return code from
--fast- Tells
DocuCheckto omit some slow operations, like pulling changes from a repository branches. - This option is useful for situations, where you’re debugging your documentation and you have already your data available locally.
- Note that
DocuCheckwill always perform slow operations if the required data is missing (like repo is not cloned yet, or branch in repo is not available yet)
- Tells
--fetch=repoor-f repo- Tells
DocuCheckto fetch changes only for requiredrepo. Other repositories will be processed like with using--fastswitch. - You can use this option for multiple repositories for the same command.
- Tells
--test=pathor-t path- Tells
DocuCheckto use local path as a source for the repository. The repository identifier is determined from the last path component. - In case that repository identifier cannot be determined from the last path component (e.g. you have cloned your sources on a custom path), then use
--testReposwitch before--test - You can use this option for multiple repositories for the same command.
- It’s recommended to use
--fastswitch when you testing your locally changed documentation.
- Tells
--testRepo=repoor-tr repo- Tells
DocuCheckto userepoas repository identifier for the subsequent--test=pathoption. - This swith can be used only in combination with
--testor-toption.
- Tells
--verboseor-v2- Tells
DocuCheckto print more debug information to the console. - You can use this switch in case of troubles, to investigate more about what’s wrong.
- Tells
--quietor-v0- Tells
DocuCheckto do not print information to the log at all.
- Tells
Examples
DocuCheck -c Config.json
Runs docucheck with configuration which must specify a paths to a repository cache and output directory.
DocuCheck -c Config.json --verbose
Runs docucheck with configuration which must specify a paths to a repository cache and output directory and increases verbosity of the command.
DocuCheck -c Config.json --failOnWarning ; echo $?
If any WARNING is reported by the tool, then the return code from the tool will be non-zero.
DocuCheck -c Config.json --showUnusedDocs
At the end of the execution prints all files with no external reference. You can find a possible unused documentation files with this option.
DocuCheck -c Config.json --showExternalLinks
At the end of the execution prints all external links found in the documentation. You can manually find suspicious links which cannot be detected automatically. For example, if you rename one of your projects, then you can check whether there’s no residual link missing in the documentation.
DocuCheck -c Config.json -f powerauth-mobile-sdk -f ssl-pinning-ios
During the documentation collection, only
powerauth-mobile-sdkandssl-pinning-iosrepositories will be properly updated from its remote git repositories.
