Activation via Activation Code
The most straight forward activation type is “activation via the activation code”. The activation code is a random one-time token value with limited time span associated with the particular user. Typically, the activation code is displayed as a QR code in the Internet banking, at branch kiosk, or ATM, or - as a less secure but more convenient alternative - it can be sent via SMS message or e-mail.
Example User Flow
From the user perspective, activation via activation code is performed as a sequence of steps in the mobile app and Activation Code Delivery Application (i.e., in web Internet banking). The following steps (with possible user interface alterations) should be performed:
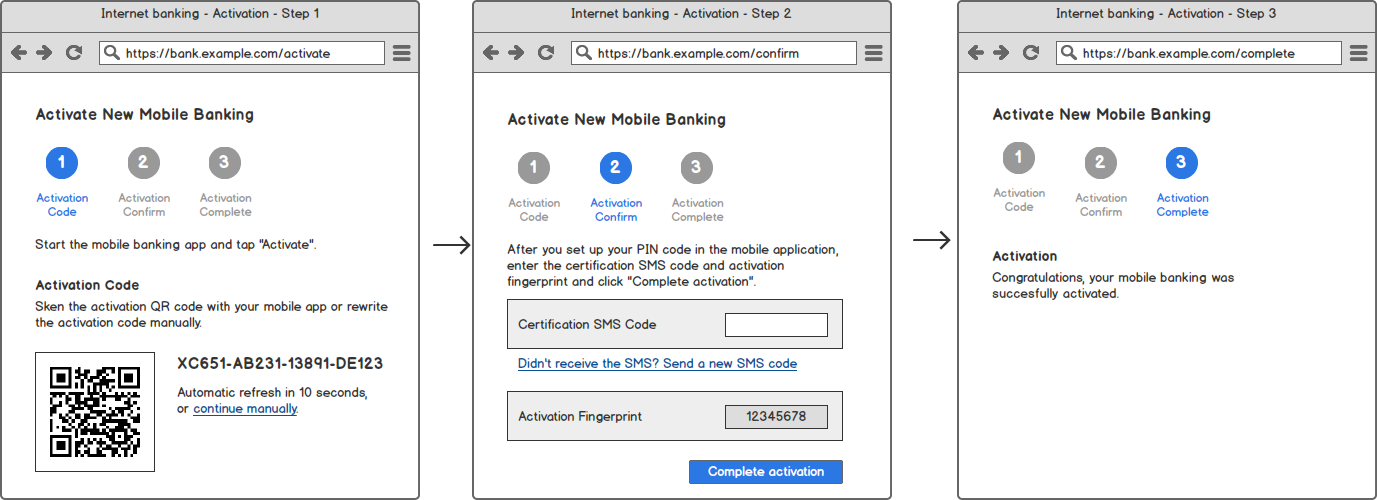
Activation Code Delivery Application
The following diagram shows example steps in the Internet banking as an example application. You can apply similar principles to other Activation Code Delivery Applications, such as branch kiosk.
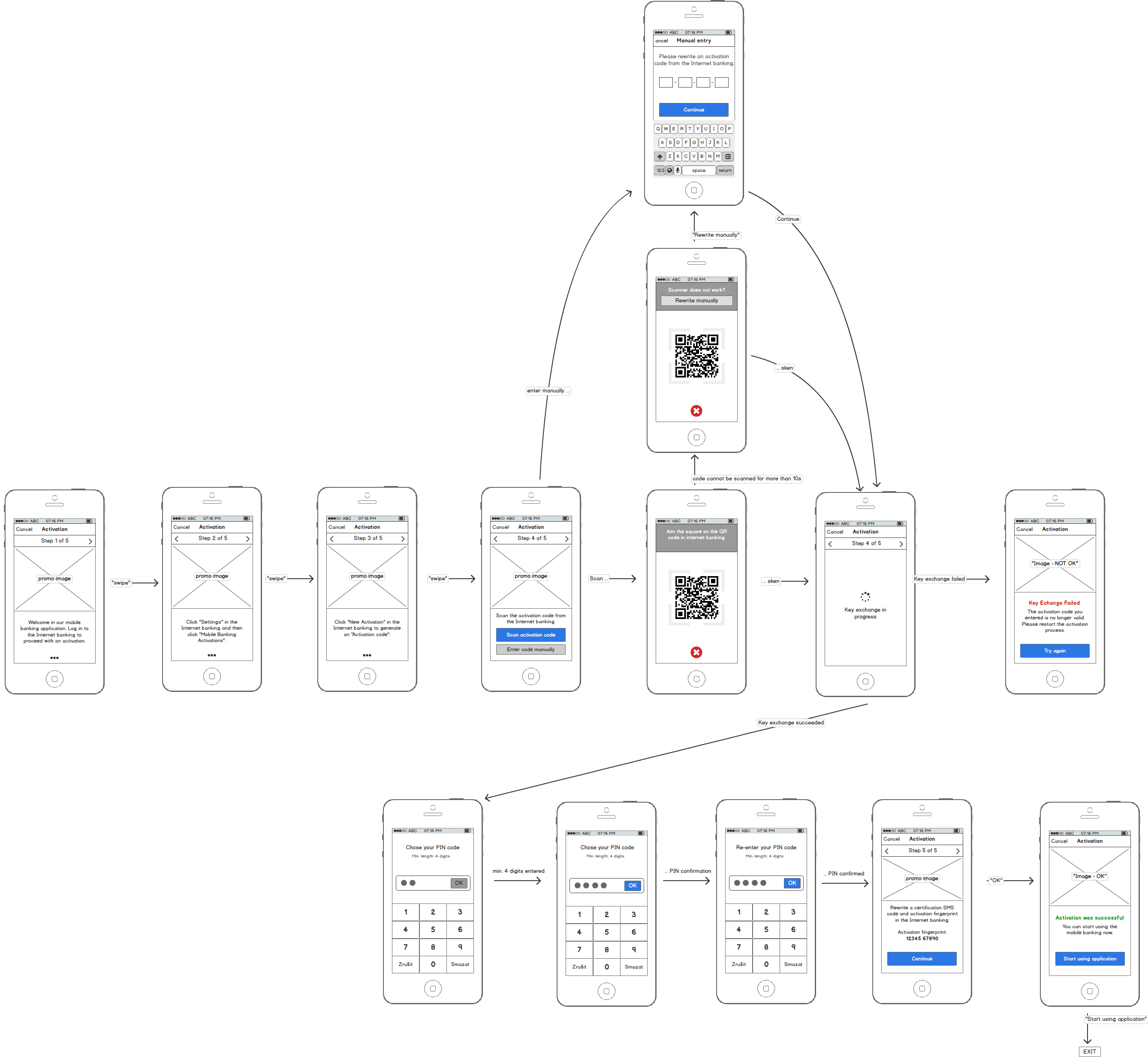
Mobile Application
The following diagram shows example steps in the mobile banking app.
Sequence Diagrams
The sequence diagrams below explain the PowerAuth key exchange during the activation via activation code. It shows how an app with PowerAuth Mobile SDK, Enrollment Server, Activation Code Delivery Application and PowerAuth Server play together in order to establish a shared secret between the client mobile application and the PowerAuth Server.
For the sake of the simplicity, we have split the process into three diagrams.
Activation Initialization
This diagram shows how the Activation Code Delivery Application requests the activation data from the PowerAuth Server. The process is initiated by the Activation Code Delivery Application (for example, the Internet banking in the web browser) and it also ends here: by displaying the activation data so that they can be entered in the mobile app and passed to the PowerAuth Mobile SDK.
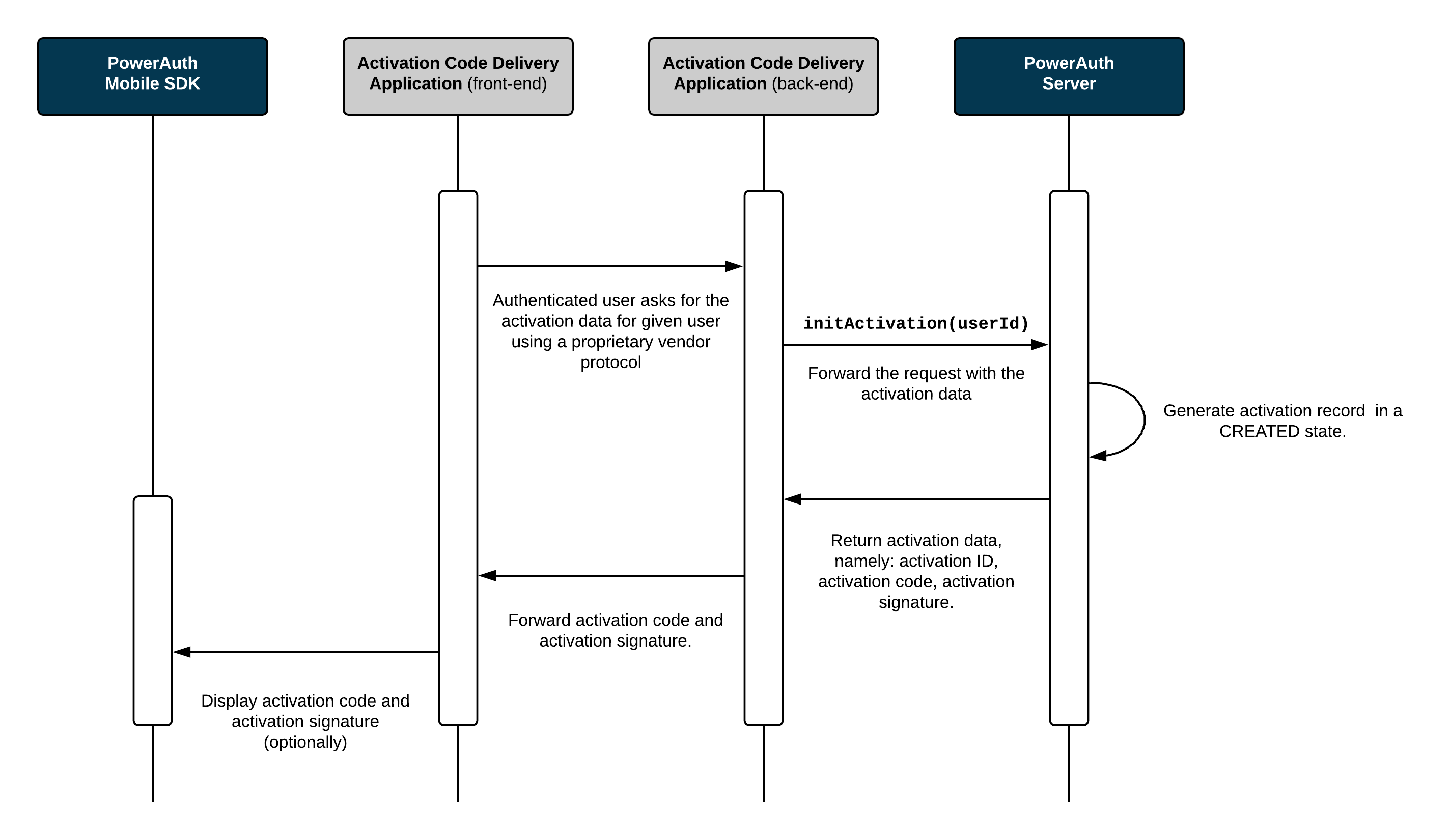
Process Description
-
The Activation Code Delivery Application requests a new activation for a given user.
- PowerAuth Server generates an
ACTIVATION_ID,ACTIVATION_CODE,CTR_DATA- an initial value for hash based counter, and a key pair(KEY_SERVER_PRIVATE, KEY_SERVER_PUBLIC). Server also computes a signatureACTIVATION_SIGNATUREofACTIVATION_CODEusing servers master private keyKEY_SERVER_MASTER_PRIVATE.String ACTIVATION_ID = Generator.randomUUID() String ACTIVATION_CODE = Generator.randomActivationCode() // must be unique among records in CREATED and PENDING_COMMIT states byte[] CTR_DATA = Generator.randomBytes(16) KeyPair keyPair = KeyGenerator.randomKeyPair() PrivateKey KEY_SERVER_PRIVATE = keyPair.getPrivate() PublicKey KEY_SERVER_PUBLIC = keyPair.getPublic() byte[] DATA = ByteUtils.encode(ACTIVATION_CODE) byte[] ACTIVATION_SIGNATURE = ECDSA.sign(DATA, KEY_SERVER_MASTER_PRIVATE) -
Record associated with given
ACTIVATION_IDis now inCREATEDstate. - Activation Code Delivery Application receives an
ACTIVATION_CODEandACTIVATION_SIGNATURE(optional) and displays these information visually in the front-end so that a user can rewrite them in a mobile app with PowerAuth Mobile SDK.
Key Exchange
This diagram shows how public keys are exchanged between the PowerAuth Mobile SDK and PowerAuth Server, and how the master shared secret and PowerAuth Standard Keys are derived.
The Activation Code Delivery Application plays no active role in the process of a key exchange.
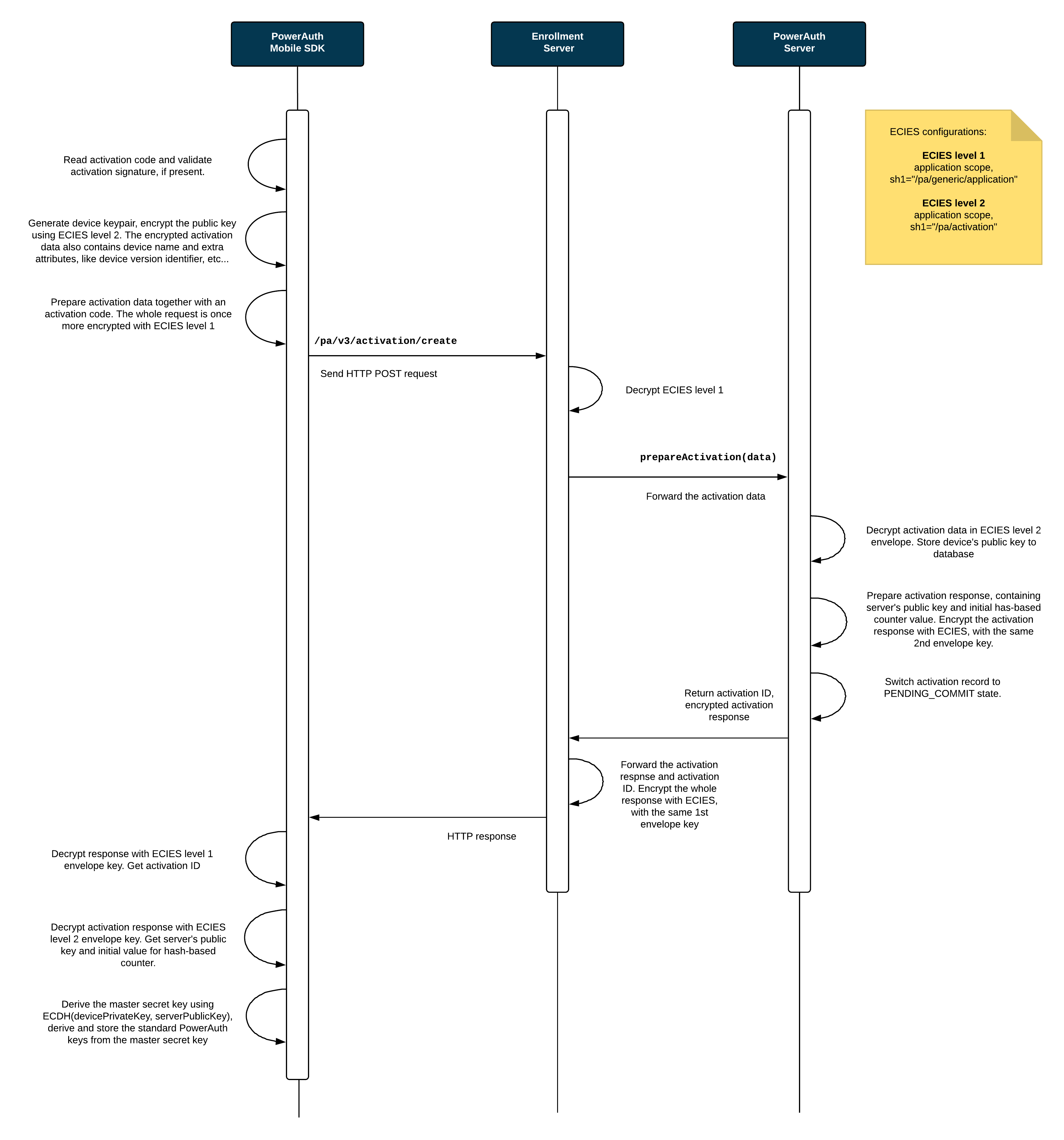
Process Description
-
User enters the
ACTIVATION_CODEandACTIVATION_SIGNATURE(optional) in the app with PowerAuth Mobile SDK. The entry can be manual or using a QR code with activation data. - PowerAuth Mobile SDK verifies the
ACTIVATION_SIGNATUREagainstACTIVATION_CODEusingKEY_SERVER_MASTER_PUBLICand if the signature matches, it proceeds.byte[] DATA = ByteUtils.encode(ACTIVATION_CODE) boolean isOK = ECDSA.verify(DATA, ACTIVATION_SIGNATURE, KEY_SERVER_MASTER_PUBLIC) - PowerAuth Mobile SDK generates its key pair
(KEY_DEVICE_PRIVATE, KEY_DEVICE_PUBLIC).KeyPair keyPair = KeyGenerator.randomKeyPair() PrivateKey KEY_DEVICE_PRIVATE = keyPair.getPrivate() PublicKey KEY_DEVICE_PUBLIC = keyPair.getPublic() -
PowerAuth Mobile SDK encrypts the payload containing
KEY_DEVICE_PUBLICwith an application scoped ECIES (level 2,sh1="/pa/activation"). Let’s call the result of this step asACTIVATION_DATA. -
PowerAuth Mobile SDK encrypts payload containing
ACTIVATION_DATAandACTIVATION_CODEwith an application scoped ECIES (level 1,sh1="/pa/generic/application") and sends HTTPS request to the/pa/v3/activation/createendpoint. -
Enrollment Server decrypts the ECIES envelope, with an application scoped ECIES (level 1,
sh1="/pa/generic/application") and calls PowerAuth Server withACTIVATION_DATA. At this step, theACTIVATION_CODEis be used to identify the pending activation. -
PowerAuth Server receives
ACTIVATION_CODEandACTIVATION_DATAfrom Enrollment Server. TheACTIVATION_CODEidentifies the record for a pending activation. If the record is unknown, then server returns a generic error. -
PowerAuth Server decrypts
ACTIVATION_DATAusing an application scoped ECIES (level 2,sh1="/pa/activation") and storesKEY_DEVICE_PUBLICat given record. - PowerAuth Server generates its key pair
(KEY_SERVER_PRIVATE, KEY_SERVER_PUBLIC).KeyPair keyPair = KeyGenerator.randomKeyPair() PrivateKey KEY_SERVER_PRIVATE = keyPair.getPrivate() PublicKey KEY_SERVER_PUBLIC = keyPair.getPublic() - PowerAuth Server uses
KEY_DEVICE_PUBLICandKEY_SERVER_PRIVATEto deduceKEY_MASTER_SECRETusing ECDH.KEY_MASTER_SECRET = ByteUtils.convert32Bto16B(ECDH.phase(KEY_SERVER_PRIVATE, KEY_DEVICE_PUBLIC)) -
PowerAuth Server changes the record status to
PENDING_COMMIT. -
PowerAuth Server encrypts response, containing
ACTIVATION_ID,CTR_DATA,KEY_SERVER_PUBLICwith the same key as was used for ECIES level 2 decryption. This data is one more time encrypted by Enrollment Server, with the same key from ECIES level 1, and the response is sent to the PowerAuth Client. -
PowerAuth Mobile SDK decrypts the response with both levels of ECIES, in the right order and receives
ACTIVATION_ID,KEY_SERVER_PUBLIC,CTR_DATAand stores all that values locally in the volatile memory on the device. - PowerAuth Mobile SDK uses
KEY_DEVICE_PRIVATEandKEY_SERVER_PUBLICto deduceKEY_MASTER_SECRETusing ECDH.KEY_MASTER_SECRET = ByteUtils.convert32Bto16B(ECDH.phase(KEY_DEVICE_PRIVATE, KEY_SERVER_PUBLIC))
Activation Commit
Finally, the last diagram shows how the Activation Code Delivery Application proactively checks the status of the activation and allows its completion by committing the activation record. A PowerAuth Mobile SDK plays a very little role in this step. It only allows showing a public key fingerprint in the mobile app to the user so that the key exchange can be visually confirmed before committing the activation.
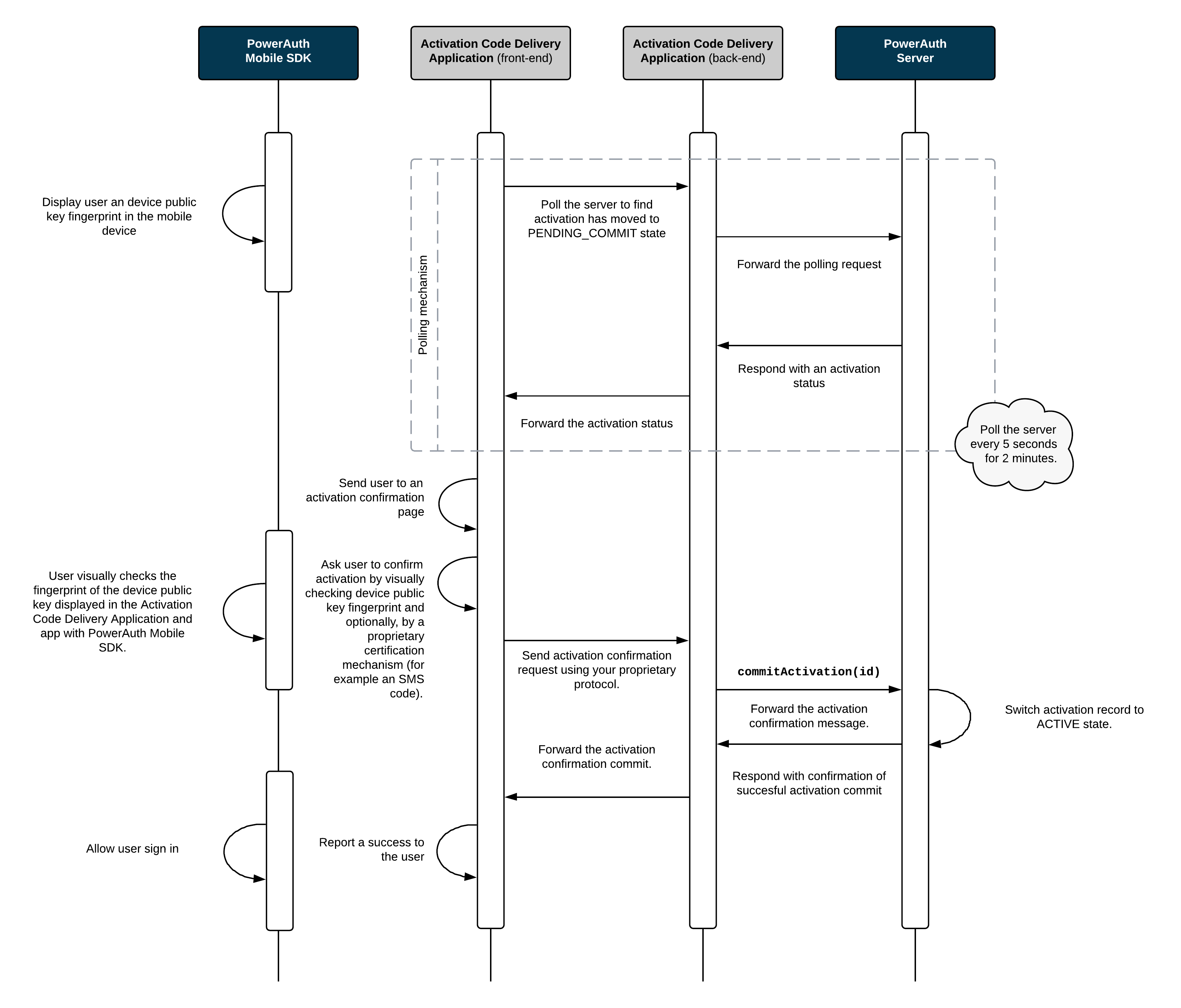
Note that the activation commit step can be skipped in case activation is committed during key exchange, as described in chapter Advanced Activation Flows.
Process Description
- PowerAuth Mobile SDK displays
H_K_DEVICE_PUBLIC, so that a user can visually verify the device public key correctness by comparing theH_K_DEVICE_PUBLICvalue displayed in the Master Front-End Application.byte[] activationIdBytes = ByteUtils.encode(ACTIVATION_ID) byte[] fingerprintBytes = ByteUtils.concat(K_DEVICE_PUBLIC_BYTES, activationIdBytes, K_SERVER_PUBLIC_BYTES) byte[] truncatedBytes = ByteUtils.truncate(Hash.sha256(fingerprintBytes), 4) int H_K_DEVICE_PUBLIC = ByteUtils.getInt(truncatedBytes) & 0x7FFFFFFF) % (10 ^ 8)
Note: Client and server should allow checking the public key fingerprint before committing the activation. This is necessary so that user can verify the exchanged information in order to detect the MITM attack.
-
Activation Code Delivery Application allows completion of the activation. For example, it may ask the user to enter an OTP code delivered via an SMS message. Activation Code Delivery Application commits the activation by calling the
/pa/v3/activation/commitservice on PowerAuth Server. -
Record associated with given
ACTIVATION_IDis now inACTIVEstate.
Related Topics
- Activation Code Format
- Activation via Recovery Code
- Activation via Custom Credentials
- Checking Activation Status
- Key Derivation
- Advanced Activation Flows
